What is Telehealth? Telehealth in layman’s terms using telecommunication technology to provide clinical services remotely to patients. Information communication technology has a great capacity to serve the challenges in developing and developed countries to make healthcare services better. With the use of telecommunication technology healthcare services are now able to overcome geographical barriers.
Being a leading mobile app development company in the UK, our professional’s app developers are acquainted with about latest technologies in telehealth app development. This is particularly beneficial for the underserved rural communities who suffer due to a lack of accessibility of health care. In primary care, the patient seeks non-emergency medical consultations which do not require the physical presence of a patient for diagnosis. Technological innovations and new advancements in Information Communication Technology telehealth facilities are also advancing and adapting this new age solution to the inaccessibility of healthcare systems throughout the globe.
The term telemedicine was coined in the 1970s which means “healing at distance”, telemedicine and telehealth are distinguished on the basis their scope telemedicine is specifically restricted to clinical services provided by physicians whereas telehealth signifies the broader scope for health services provided by health professionals (like nurses, pharmacists, and others) in generals and also focuses on non-clinical services. But because of the similarity they are often synonymous and are sometimes used interchangeably.
What is the Classification of Telehealth Services?

There are mainly three types of telehealth services:
Remote Monitoring: it is also known as self-monitoring. It uses different monitoring devices to collect clinical data of a patient’s health for diagnosis of chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases or asthma. It is a cost-effective method, includes regular and consistent monitoring with greater patient satisfaction. Although there are chances of data being inaccurate because tests are self-conducted.
Realtime Interactive Services: Patients that require medical attention meet doctors virtually on a video conferencing platform. Doctors diagnose their patients based on their medical history, current symptoms and live assessment similar to physical examination in a clinic or a hospital. Some applications of real-time interactive services are:-
- Telenursing
- Tele neuropsychology
- Tele pharmacy
- Telerehabilitation
Store and forward: it is also called asynchronous telemedicine; it surpasses the need for an appointment and a physical examination. Documented patient information like lab scans, imaging studies and test reports are acquired by patients and are sent to a specialist for an examination. This practice is common in ophthalmology, radiology and pathology. This method saves time and allows practitioners to collaborate and conveniently review the information. The patient also has access to a better consulting team in different locations.
What is the History of Telehealth?
The origin of telehealth can be traced back to the mid to late 1900s, in Pennsylvania radiology images were sent in the 1940s via telephone line between two towns is said to be the first medical record transfer. Later in the 1950s, a Canadian doctor constructed a teleradiology system that was used in Montreal. These practices became widespread with advances in motion pictures and modern film technology.
Clinicians at the University of Nebraska first used video communications for medical purposes, in 1959 the University used a two-way TV setup for video consultations. There are many examples of primitive telehealth services (i) discussions between psychiatric experts and general practitioners at state mental hospitals (ii) specialist consultation from a major hospital to airport medical centre.
Major ICT advancements in the 21st century have been the biggest push to the telehealth industry. Innovations and inventions over the past decades have rapidly created new possibilities for healthcare advancements in telehealth.
Telehealth System Application:
Telehealth services use customized applications for mobiles, PCs, and kiosks. They look similar to consumerized video conferencing software like skype, zoom, duo etc. but are very different.
How do Telehealth software work?
Telehealth requires four main things:
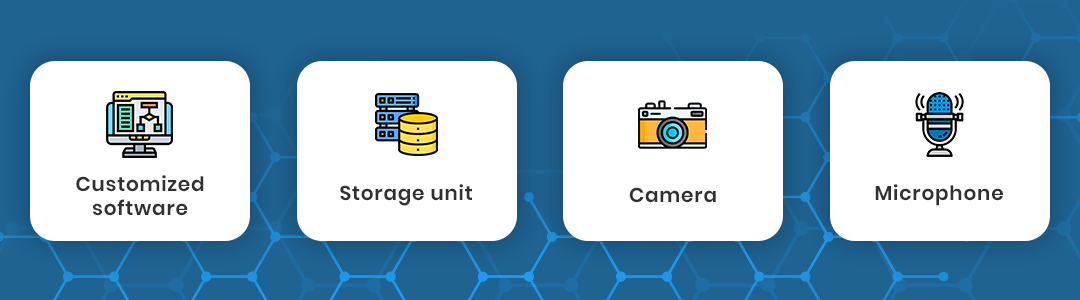
- A customized software
- A storage unit
- A camera
- And a microphone
We need customized software to connect health experts and patients and guide information input of patients to storage. The camera and microphone are used in interaction.
Telehealth system applications can be divided into three different categories:

Online video conference: online video conferencing is the most common type of telehealth service. We need a secure customized platform for doctors and patients to interact. Through video conferences, doctors can diagnose their patients in real-time and can provide accurate analyses of their health issues.
Treatment advice: this is more of a question-and-answer platform but about the patients’ existing treatment plan. If a patient has any queries regarding his existing treatment plan, he can drop a text message.
Prescription management: this helps a patient to get drugs prescription online. The patient has to apply for a prescription based on his medical history or recent diagnosis physicians can decide prescriptions. After getting it through he can easily take drugs from a local pharmacy.
Advantages of Telehealth App:

Accessibility: telehealth is fueled by digital technologies and it can be used to reach high-risk rural and remote areas where there is a lack of good healthcare services.
New business model: By improving consumer-based care, telehealth as a commercial model is experiencing a paradigm shift. With help of telehealth, clinicians can expand their patient base with their platforms.
Cost Efficient: telehealth can cut a major portion of patient costs. Travelling long distances to a doctor’s clinic can be stressful and can add to the costs. With telehealth doctors and patients can meet virtually on their phones or other devices.
Improves Healthcare Qualities: telehealth improves healthcare conditions particularly in rural areas by improving service delivery and treatment of acute conditions. It is also convenient for the patients to receive without travelling long distances.
Patient satisfaction: it is a key indicator for the success and promotion of telehealth services. Ortholive telemedicine app development in the US reported an 87% of patient satisfaction rate.
Telehealth apps keep records of your every visit and any previous information you provided in a maintained EHRs database which saves time.
Disadvantages of Telehealth App:
Telehealth saves you travel and gives you accessibility to specialists, but it does have a few downsides too:
Technical training and Equipment: change in the method requires a change in staff responsibilities too, training is crucial to an effective telehealth program physicians and other medical staff need to be trained on a new system to work efficiently.
Security of patients’ information on telehealth platforms is a concern as the data is transmitted electronically through the internet. The patient’s confidentiality may be violated.
Reduced Continuity of Care: in case a patient uses on-demand services and is appointed a random care provider with an incomplete history of the patient and may not have records or notes of his/her previous visits care continuity suffers.
Every sort of visit cannot be performed remotely. We must visit diagnostic centers for different tests, as well as evaluations that require a more hands-on approach.
Telehealth Application development:
A telehealth application program has two sides for doctors and patients. A telehealth application must be user friendly on both sides to make consultation easier and hassle-free.
Telehealth app features for patients:
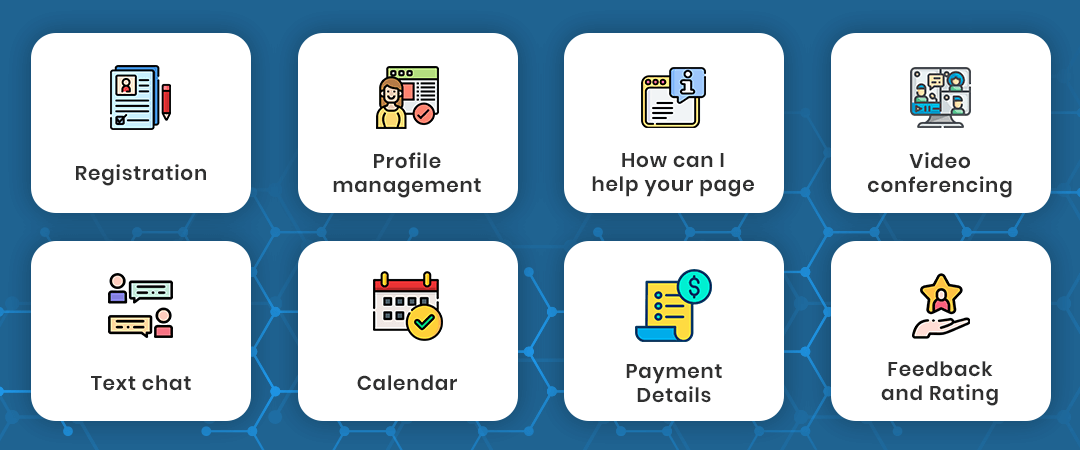
Registration: The first need of any platform is to know who is accessing it. Through registration, your login id is made so that you can maintain your account and change your personal details. Sometimes the app may require any relevant photo id proof. Patients can sign in via email ids.
Profile management: After the sign-in patient has to fill in their personal profile details like name, age, gender, height, weight, etc. Patient’s electronic health records are made.
How can I help your page: it is similar to a search box but you will be asked to answer some general questions about your problems or health issues so that the system can assign you a specialist.
Video conferencing: a video conferencing feature allows your doctor to examine you more thoroughly. Make sure that your internet connection is optimized.
Text chat: text chat is for minor issues or to answer your queries related to your treatment plan
Calendar: in-app calendar is used to make schedules and appointments. It is also used in monitoring your treatment. You can also sync it with your device calendar.
Payment Details: a secure payment gateway is a vital feature. You can either make a custom gateway or you can use a third-party gateway like PayPal.
Feedback and Rating: you can create a rating system combined with feedback for the patient’s experience with the doctor. Patient Satisfaction is necessary for improvement in your telehealth services.
Telehealth app features for doctors:
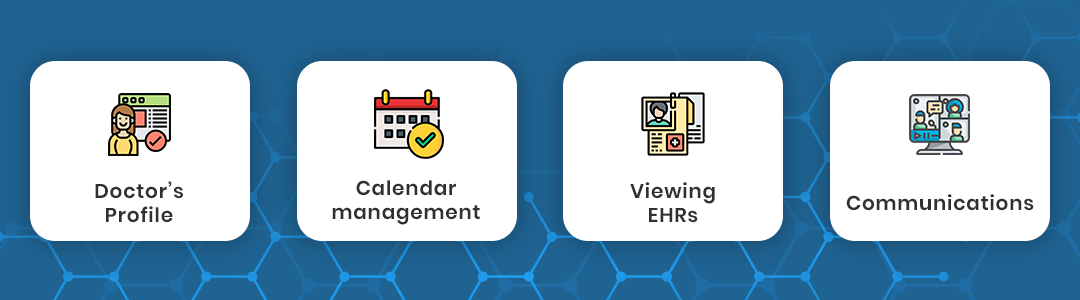
Doctor’s Profile: Information such as their education, specialization, medical competencies, experience, and other information about their practice.
Calendar management: this feature makes it easy for a doctor to make appointments with his patients and make his availability known.
Viewing EHRs: doctors can access the EHRs of their patients. With previous records, they will be able to make more accurate diagnoses.
Communications: a two-sided communication is necessary; doctors should be able to check up on their patients.
What are the technologies involved in telehealth apps?
Telehealth is the future and solution to many problems in our healthcare systems. The present disaster of COVID-19 made it evidently clear that we need telehealth and what are its drawbacks. And to make things better some modern technologies can upgrade the existing telehealth platforms. Below mentioned technologies are some examples of how we can improve the mobile applications of telehealth.
Artificial Intelligence: automation of routine processes can relieve doctors some of their workload. FAQ chatbots can answer the usual questions about availability or scheduling or a query about trivial health problems. If we use machine learning it can also help doctors make better diagnoses. It can also recommend treatments using data analysis.
Cloud Storage: A telehealth service application will have a lot of new data generated every day. You can store it in hard drives if you need large space to build a server and a lot of hardware, or you can use Cloud storage (which lets you store data on remote servers accessible through the internet) services of any third party.
Blockchain: biggest concern of clients is whether their data will be safe or not with all the sensitive data on the internet blockchain encrypts your data in a way that makes it difficult to change the information stored.
Internet of Things: It is a perfect match for remote monitoring of patients with compact Fitness bands, stress monitors and scales and other devices collecting data makes it easy for doctors to make better treatment plans. With all-time wearable devices data is more precise.
Data analytics: telehealth generates large amounts of EHRs and also contains the previous records of patients. Big Data is an outcome-oriented model which provides a more holistic way to approach a patient’s health.
Auxano Global Services is one of the leading global IT applications development companies in UK that specialise in creating state of the art mobile applications. They boast about their immaculate outcome in building telehealth applications from scratch. They provide full stack end to end cost-effective application development right from conceptualisation to end with the maintenance and housekeeping of the application while it is in use.



![Complete Guide to Create Decentralized Apps (Dapps) [2023]](https://auxanoglobalservices.co.uk/new/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/Front-506x289.jpg)